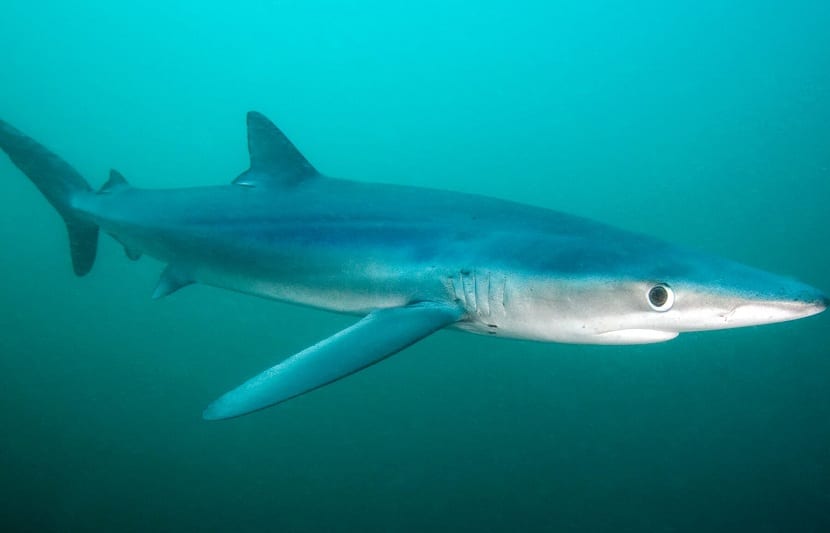
Today we come to tell you about another species of shark that will surely fascinate you. Its about blue shark. It is a type of cartilaginous fish that belongs to the Carcharhiniformes and the Carcharhinidae family. It is known by the name of tintorera. It is one of the most hunted sharks in the world, although in its time it was one of the most abundant in all the seas and oceans. Therefore, we are going to dedicate the importance it requires in this post.
Do not miss all the biology, characteristics and way of life of the blue shark.
Key features
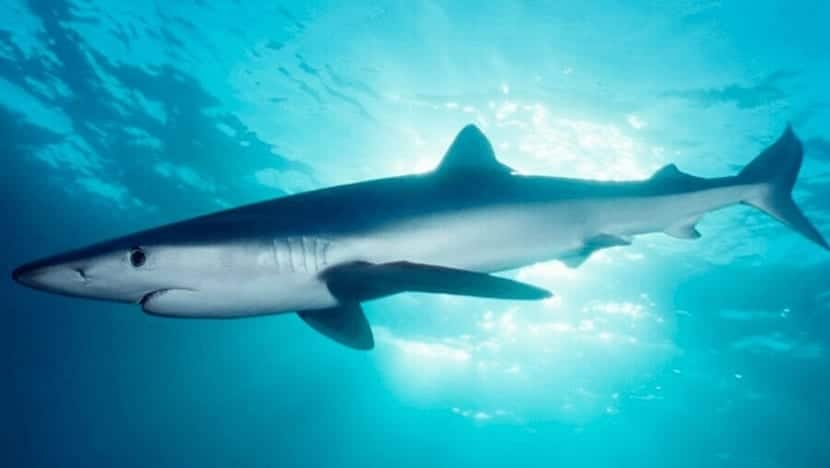

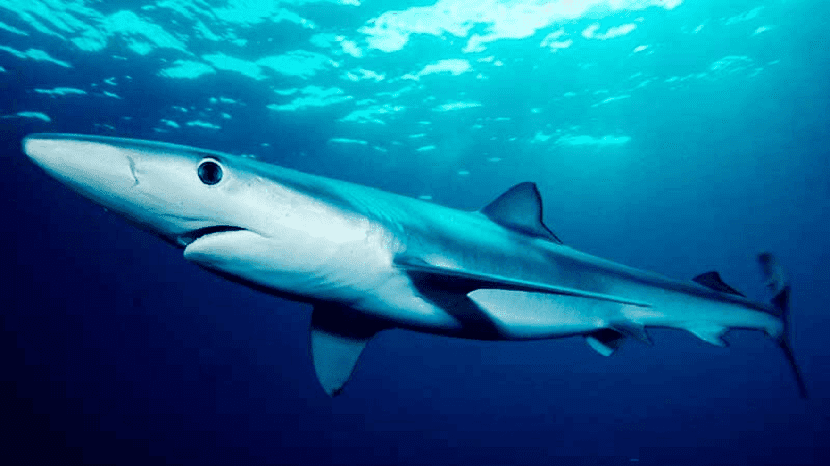
It is a species that is not too large in size. The body measures close to 4 meters and length. As usual the male is between 1,80 and 2,2 meters, while the female grows between 2,2 and 3,3 meters. It is rare to see specimens that measure 4 meters. Its body is quite slim, which makes it a fairly agile and hydrodynamic shark.
In the male, the weight ranges between 27 and 55 kilos while the female between 93 and 182 kilos. As you can see, it is a very noticeable difference, which makes it easy to differentiate between the sexes. As for its color, its name says it, blue. The distinctive indigo coloration on the back makes a nice contrast to the light gray on the underside. On the sides they have a brighter blue color.
The eyes are quite large and its muzzle has a conical shape. Its teeth have jagged edges to better grind food. While the teeth on the upper part are triangular and hooked, those on the lower jaw have a straighter and narrower shape. Each tooth is replaced in periods of between 8 and 15 days.
Their pectoral fins are quite long when compared to those of many other species of sharks. The second dorsal fin is smaller than the first. As for its tail, it is quite long, which makes it have a very good swimming ability. They are capable of swimming at great speeds and, having great agility and a slim body, they become very feared predators.
Distribution and habitat
This animal is widely distributed around the world. We find it natively in the Atlantic Ocean, the Pacific, the Indian Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Its habitat is the epipelagic and mesopelagic zones of the deepest waters. It can usually be found swimming at depths of 350 meters. It prefers temperate and tropical waters in these oceans since these temperatures favor them more.
Behavior of the blue shark
Although the blue shark prefers to be on the surface of the deep water, at night it ventures to swim closer to shore. It is a solitary animal but it has migratory behaviors. When he travels and travels long distances, he does not travel alone, but rather in a group. For example, you can swim all the way from New England to South America. If you do these migrations you follow the coriolis force of the ocean currents. That is, if you travel across the Atlantic, you follow the clockwise pattern. That is, it passes from the Caribbean Gulf Stream to the east coast of the United States and Europe. Then it passes through southern Africa and finally returns to the Caribbean Sea. This is more or less his migration itinerary.
Sometimes we see them forming groups according to sex and size. The role of staying in groups is not known for sure.
Feeding and reproduction of the blue shark
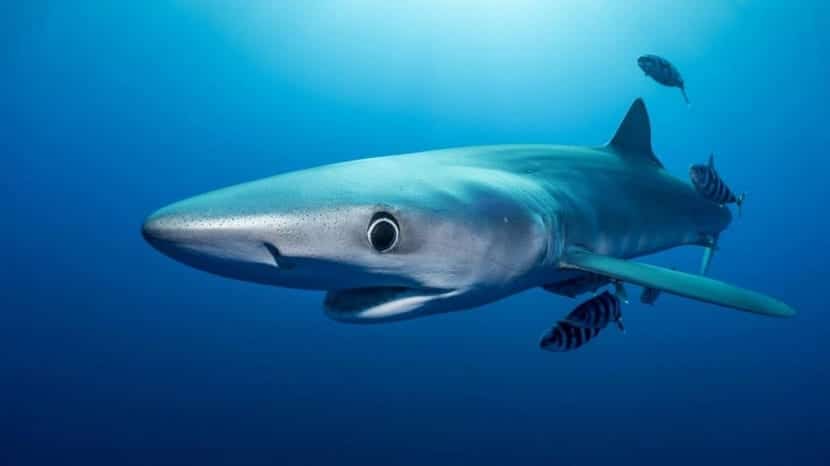

Now let's move on to your diet. It is a shark with predatory habits. We can see that it feeds basically de peces and mollusks. Among their most basic diet we find anchovies, sardines, herring and squid, which is their favorite. On some occasions it feeds on mammal corpses if the rest of the food is lacking. Sometimes in its passage it encounters seabirds.
In total we find about 24 species of cephalopods and 16 species de peces.
Regarding its reproduction, we have a viviparous fish that usually has between 25 and 50 offspring. Sometimes more than 100 offspring have been recorded from a single female. The age at which sexual maturation begins begins between 4 and 5 years in males and 5 and 6 years in females. Being of a greater size and weight, they take longer to reach maturity.
These sharks have a courtship rite that includes bites from the male to the female between the first and second dorsal fins. The female does not receive damage since her skin is 3 times thicker than that of the male. This is how the male inseminates the female by inserting a clamp into the urogenital opening. It transmits the sperm and after mating both sharks separate. The young develop within a placental sac. Gestation lasts between 9 and 12 months. When the young are born, they are only about 39 centimeters tall. They have no parental care. As soon as they are born they separate and grow on their own.
Threats
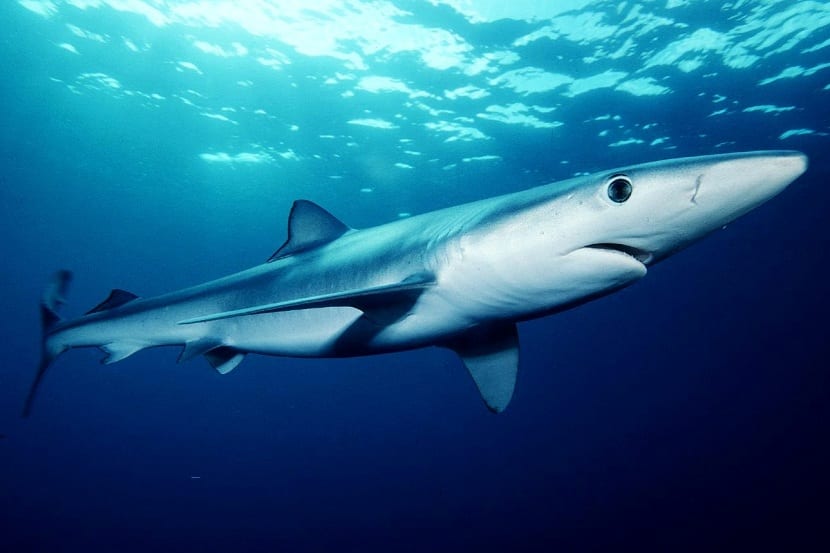

As we have mentioned before, the blue shark is in the "near threatened" category because it is heavily hunted around the world. Human activities, attacks on young individuals of other larger predators, and accidental hunting cause populations to be detrimental.
The fins of this shark are used to make a soup highly coveted in gastronomy for its supposed aphrodisiac powers. Good quality food supplements are made from your liver.
The main concern is the drastic reduction that populations are suffering. In just the Mediterranean Sea, it has dropped 97% since the XNUMXth century.
I hope that with this information you can learn more about the blue shark and its way of life. Let us hope that populations do not continue to decline due to accidental hunting.