One of the fundamental biological processes in living beings and, above all, for those that inhabit aquatic ecosystems is the osmoregulation, Also known as osmotic balance.
All metabolic reactions necessary for life take place in an aqueous or liquid medium. For the correct operation of these reactions, it is necessary that the concentrations of water and solutes (all those low molecular weight organic compounds that help maintain the osmotic balance) oscillate within relatively narrow margins, in a process called osmoregulation.
We can define the osmoregulation as the method that maintains the homeostasis of the body, which is nothing other than the ability of living organisms to keep their internal condition stable as a function of the changes that may occur abroad through the exchange of matter and energy with the same.
All of this crucially depends on the controlled displacement of solutes in internal fluids and those in the environment. This leads us to the regulation of the movement of water playing a fundamental role.
This regulation of the movement of water is carried out by osmosis, which is a physical phenomenon based on the movement of a solvent liquid which passes through a semi-permeable membrane. This phenomenon arises thanks to a simple diffusion that does not require energy expenditure and that becomes crucial for the correct cellular metabolism of living beings.
In short, and as a general summary, the osmoregulation helps us make the concentrations of solutes existing inside organisms (example: cells) and the environment that surrounds them, tends to balance itself through movement and flow that crosses a semi-permeable membrane. Such a circumstance allows us to regulate the osmotic pressure (pressure exerted on in order to stop a certain flow of solvent that penetrates a membrane).
Osmotic balance in animals

In most animals, the fluids that supply cells are isosmotic compared to fluids that coexist inside cells. What does this mean? Well, the fluids inside and outside the cells have a osmotic pressure very similar. This is to prevent the cell from swelling excessively, as would occur in a hypotonic solution, or wrinkling, something that happens in the hypertonic solutions.
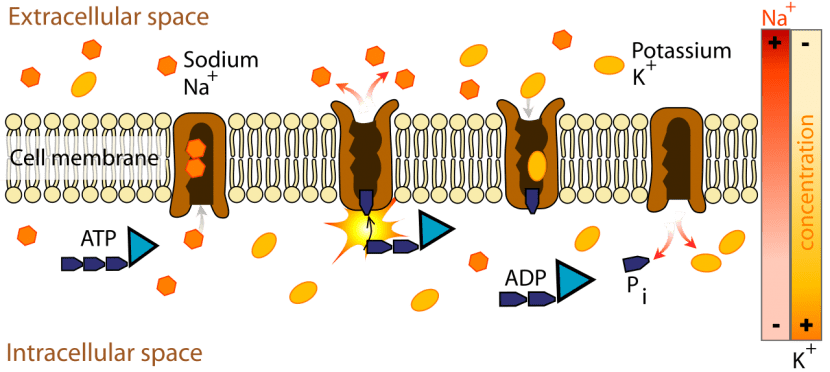
To be able to keep those fluids isosmotic On both sides of the plasma membrane, what they do is use large amounts of energy with which they manage to pump Na + from inside the cell out through active transport.
Animal cells see in a solution isosmotic a suitable medium for its proper functioning and development. On the other hand, in the plants it is not like that. Plant cells found in a solution isosmotic They can suffer a strong loss of turgor, since these cells are capable of retaining in their cell wall high amounts of solute with which they achieve greater volume and elasticity.
Osmorregulation in aquatic animals
Aquatic animals have managed to adapt to a wide amalgam of habitats, ranging from fresh water (with very few solutes) to high salinity water (huge amounts of solutes). This has caused them to have to face problems of regulation of the osmotic balance very disparate from each other. In addition, it is worth mentioning that each species or organism functions within a range of osmotic concentration of the given environment.
In this case, we can distinguish between:
- Pinholes: organisms that tolerate a narrow range of salinity typical of the external environment, regardless of whether it is fresh water or salt water.
- Euryhalines: organisms that tolerate a much greater range of salinity typical of the external environment, regardless of whether it is fresh water or salt water.
Mainly, there are two basic ways to achieve the long-awaited osmoregulation.
In the first place we are presented with the osmoconformism, which refers to those animals that are in osmotic balance constant with the environment in which they live, becoming animals isosmitic with its natural environment. They are usually organisms that are mainly found in fresh water, although some also do so in unsafe waters that contain some salinity.
And, in the second instance, we have the animals osmoregulators, which should try to maintain that osmotic balance with their environment. This implies an energy cost that varies depending on the permeability of the skin or outermost surface of the animal. It should also be mentioned that if the osmolarity of body fluids is greater than that of the environment, we are facing an animal hyperosmotic. However, if it is much smaller, we will say that it is an animal hypoosmotic.
Osmoregulation in freshwater fish
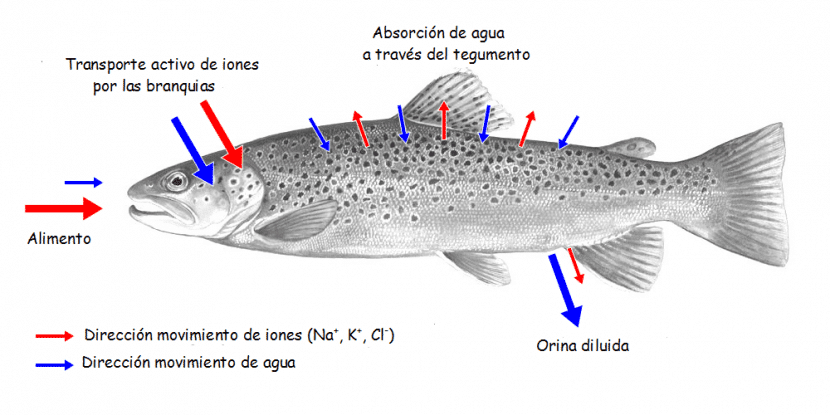
In freshwater fish, the ion concentration in the body is certainly higher than in the water. This causes a constant diffusion of water that penetrates through the epithelium of the gills and the rest of your body to the interior.
This is adjustable thanks to the fact that the kidney of this set de peces generates large amounts of urine. To this we must add that by having a concentration of salts that the water itself in which they live, they lose electrolytes, which they must compensate by absorbing salts through their gills.

Osmoregulation in saltwater fish
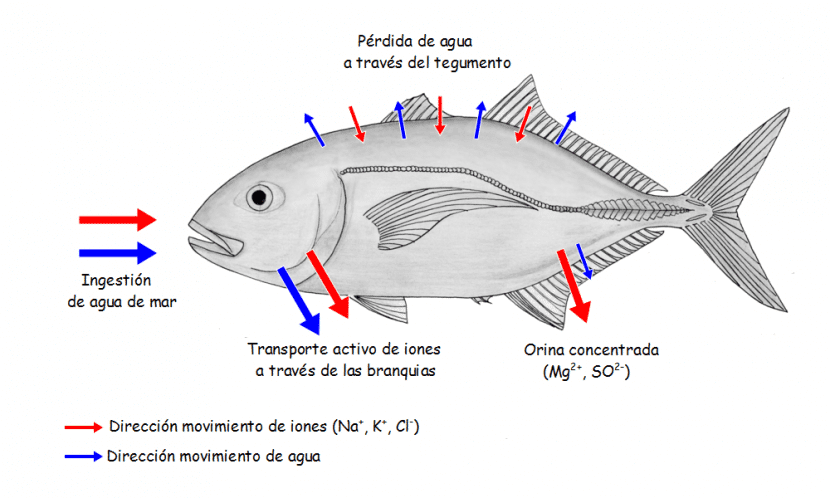
In the process of osmoregulation Of the saltwater fish, or marine fish, the opposite is true of that of their freshwater relatives. In this case, the water is constantly flowing through the inside of the fish's body going outwards. The ions that houses the water penetrate the body of this animal through the gills. This can lead to a serious problem, which is none other than the risk of dehydration.
In order to avoid dehydration, marine fish constantly ingest large amounts of water, and the excess salts that are generated are expelled to the outside through three routes: faeces, urine and the gills themselves.
El osmotic balance, a priori, it may seem something very difficult and complex to understand. However, it is crucial for life, since all organisms depend on it. It is also important that it is known by all those who love fish, since this way they can better understand the internal behavior of their animals. We hope we have been able to help you and clarify certain doubts regarding this tedious subject.